Nutritions
What Vitamins & Nutrients Are Found In Eggs?

1. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
Riboflavin – also known as Vitamin B2 – is necessary for cell growth, energy metabolism, red blood cell development, healthy vision, and the sound functioning of the nervous system. It also serves as an antioxidant nutrient, fighting damaging particles in the body known as free radicals.
Bacteria in your gut can produce small amounts of riboflavin, but not enough to meet sufficient dietary needs or store any as a backup – making the case to incorporate effective amounts in your diet even more important. To make it easy, a serving of two eggs contains 24% of your RDI of Riboflavin.
2. Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays an important role in calcium and phosphorus absorption, making it essential for the maintenance of healthy bones and teeth. More than just the ‘sunshine vitamin’, it also contributes to maintaining regular muscle function and supporting your immune system.
Now, egg yolks are one of the few foods that contain naturally high amounts of Vitamin D, with a serving of two eggs providing 82% of your recommended daily intake.
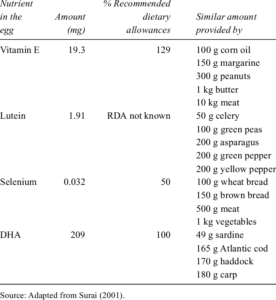
3. Vitamin E
Vitamin E has beneficial antioxidant properties that play a pivotal role in maintaining good general health – including heart health – with studies linking it to lower rates of heart disease.
Studies have also found significant links between vitamin E and immune function, helping the prevention of certain cancers, a reduction in age-related eye disorders, and slowing cognitive decline associated with ageing.
An average serving of two eggs provides 20% of your RDI of vitamin E.
4. Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5)
Pantothenic acid, commonly known as Vitamin B5, plays a significant role in converting the food you consume into active energy and breaking down fats. It also aids in the making of Vitamin D and the production of red blood cells that carry oxygen around the body.
Though uncommon when following a healthy and balanced diet, a deficiency in Vitamin B5 may result in fatigue, irritability, numbness, and muscle cramps, among other symptoms.
A serving of two eggs provides you with 22% of the RDI of Pantothenic acid.
5. Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential in the formation of red blood cells and DNA, repairing body tissue, and maintaining the healthy function of the immune and nervous systems.
Unfortunately, B12 deficiency is common, especially in the elderly sometimes leading to fatigue, weakness, weight loss, decreased appetite, dizziness, constipation, and more. As the human body is incapable of producing Vitamin B12 on its own, it’s necessary to be active in consuming foods that are a rich source of this vitamin.
The recommended daily intake of B12 is about 2µg, with a serving of two eggs satisfying 15% of your everyday requirements.
6. Vitamin A
Vitamin A is vital in sustaining healthy skin, supporting immune function, maintaining good vision and promoting general reproductive health.
Drawing sufficient Vitamin A from within your diet should prevent any symptoms of deficiency, including hair loss, skin problems, dry eyes and an increased risk of infections.
With the recommended daily intake for Vitamin A set at 750µg, a serving of two eggs delivers 14% of the advisable amount.
7. Iron
Iron is an essential dietary mineral that is involved in various primary functions, including the transport of oxygen throughout the body and providing energy for daily life.
Despite its importance, an estimated one in eight Australians is iron deficient, which can lead to a limited supply of oxygen to tissues and organs, fatigue, headaches, insomnia, and appetite loss.
With your body absorbing only a fraction of the iron within the food you eat, the case for actively consuming iron-rich meals is even more important.
One large egg contains 0.9mg of iron, found predominantly in the yolk. An average serving of two eggs provides 14% of your RDI for iron.
8. Phosphorus
Phosphorus is essential for the development and maintenance of healthy bones and teeth, filtering waste and repairing tissue and cell membranes. It also contributes to supporting energy metabolism and muscle growth.
Low levels of phosphorus can result in a loss of appetite or joint pain, and irritability or anxiety.
With adults needing around 1000mg of phosphorus per day, a modest serving of two eggs provides 21% of this daily requirement.
9. Folate
Folate is an important nutrient for people of all ages, playing a significant part in promoting red blood cell growth, the formation of DNA and supporting an effective immune system. In particular for pregnant women, folate helps in the production of new cells, protecting against serious birth defects, such as spina bifida.
It’s recommended that an average adult consume about 200µg of folate daily (more in pregnancy), and a serving of two eggs will provide 49% of your RDI.
10. Iodine
Iodine is an important mineral in helping your thyroid to produce hormones to regulate your body’s metabolic rate. It also serves in promoting cognitive function, optimal brain development and maintaining healthy skin.
Iodine deficiency can be quite common, leading to various health conditions such as swelling of the thyroid gland and ongoing fatigue.
Eating just two eggs a day helps you reach 29% of your daily recommended iodine intake.
11. Selenium
Although only required in trace amounts compared to other vitamins and minerals, selenium is an important antioxidant that helps prevent free radical damage to cells in the body. Selenium supports the immune system, thyroid gland function, and the maintenance of healthy hair and nails.
Eggs are an excellent source of selenium, with an average serving of two eggs meeting 41% of your daily recommended intake.
12. Choline
Choline is a little-known yet important nutrient that plays a vital role in brain development and function – essential in prenatal human health as well as adulthood. Choline is also used by the body to assist with liver and nerve function.
The human body can produce choline but not in the sufficient amounts needed daily by your body, meaning the rest of those needs can only be satisfied through diet.
Eggs, in particular, are a major source of choline. Two eggs can provide 77% of women’s recommended daily intake and 59% of RDI for men.
13. Lutein and Zeaxanthin
Lutein and zeaxanthin are vital antioxidants, which protect your cells from damage. Most notably, they support the clearance of free radicals and serve in protecting against eye conditions.
As carotenoids, they are naturally present in foods, especially in dark green leafy vegetables, such as spinach and kale – as well as in egg yolks. However, due to their high bioavailability and not being subject to seasonal variation, the consumption of eggs is a favourable source of lutein and zeaxanthin in the diet.
There is currently insufficient research to indicate an exact level of recommended dietary intake for lutein and zeaxanthin, although some researchers have recommended levels as high as 6mg per day.
One serve of two eggs contains around 530µg of lutein and zeaxanthin, alongside being an effective vehicle for increased and site-specific antioxidant uptake.
The essential nutrient in eggs
What are the health benefits of eggs?
It’s generally believed that eggs are the original superfood because of their many health benefits. Eggs provide good protein (especially in the egg white), vintamins, minerals, omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Wow! No wonder they’re considered a superfood. Here’s a run down of what’s contained in that shell:
- Nutrient rich – 40% of daily vitamin D requirements, 25% of daily folate, 12% of daily riboflavin (Vitamin B2), 20% of daily selenium. Plus eggs contain all important choline. More on that later.
- High-quality protein – one egg contains about 6.3g of protein. This helps build, strengthen and repair or replace things such as tissue. The protein in eggs contains all nine essecial amino acids needed by the body for optimum growth and maintenance.
- Raise levels of good cholesterol – Eggs help increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), or good cholesterol. Higher levels of HDL can help reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Good source of omega-3s – Eggs contains similar types of omega-3s as those found in fish. Which makes eggs useful for people who avoid or can’t eat fish. Omega-3 fats are good for things such as heart and brain health, and also help to protect eyes.
- Eggs are filling – because eggs are nutrient dense with high-quality portein, they are one of the healthiest food for weight management. They can increase levels of a hormone that helps you feel satisfied after eating as well as delay the rate at which food leaves the stomach. It’s the high-satiety levels of eggs that leads to greater feelings of satisfaction, less hunger and a reduce desire to eat later in the day.
What are the benefits of choline in eggs?
It’s so important for our health and it’s an essential nutrient in eggs, but many people don’t know what choline is. Results from studies are increasing our awareness and understanding of choline every day. With eggs providing some of the highest quantities of choline of any food, omelette has delved into what exactly choline is, how it benefits our bodies and where you can find this important micronutrient in your daily diet.
- What is choline? Choline is a nutrient made in the liver, however most people don’t produce enough to meet daily requirements. This means choline also needs to provided by the foods we eat. It is essential for human health and is similar in function to B vitamins. Research suggests that choline plats an important role in brain and spinal cord development during pregnance, cognitive development in infants and may also help prevent cognitive decline in the elderly.
- Choline and pregnancy Because if it’s beneficial role in developing a healthy brain and nervous system functions, choline is particularly important during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Choline also plays a role in reducing the risk of certain birth defects, as well as supporting foetal cognitive and spinal cord development.
- Benefits of choline It is an essential nutrient for the following reasons:
- helps create fats that support the integrity of cell membranes and contributes to strong cell membranes
- can help to create a substance that is essential for removing cholesterol from liver and sending it into the bloodstream to use for energy
- contributes to methylation, a metabolic process that helps your body repair and produce DNA.
- helps produce acetylcholine, which is an important neurotransmitter that is needed for muscle control, memory, focus and heartbeat regulation, among other basic functions.
- Do eggs have choline? Eggs are the most common source of choline in the Australian diet, providing more than double the amount of choline per 100g than any other commonly eaten food. One large hard-boiled egg contains 164mg of choline. This provides about 30-36% of your daily requirement. This is present only in the egg yolk. The egg white does not contain choline.
- Other foods that contain choline This nutrient can also be found in foods such as beef or chicken liver, fish, cauliflower, broccoli, brussels sprouts, cabbage, peas, tofu, quinoa and carrots.